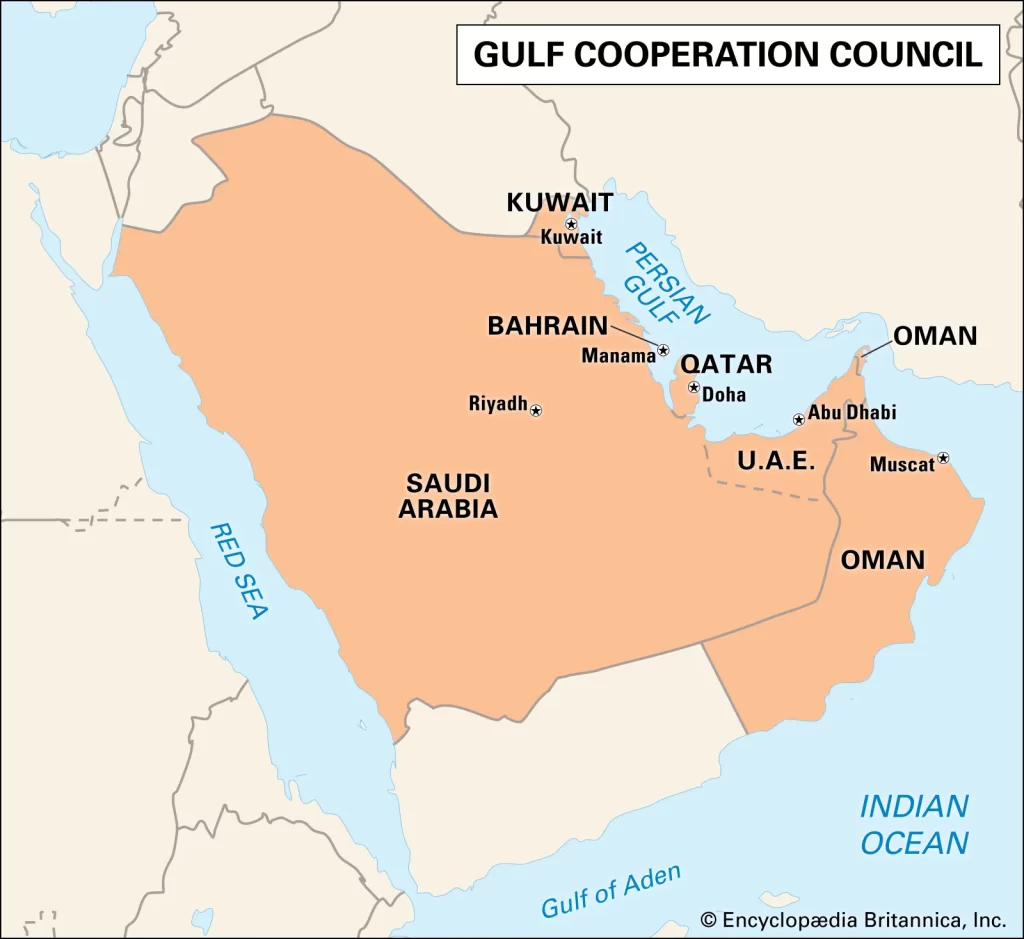
The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) is a political and economic union of Arab states bordering the Gulf. It was established in 1981 and its 6 members are the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Oman, Kuwait and Bahrain. The GCC’s prime geographical location is at the crossroads of the major Western and Eastern economies. The established and efficient air and sea connections and developed infrastructure make it a great place to establish and expand business.
| United Arab Emirates | Saudi Arabia | Qatar |
| Oman | Kuwait | Bahrain |
Gulf Cooperation Council
Since the discovery of oil, the GCC region has undergone a profound transformation and is now home to some of the fastest growing economies in the world. Today, the governments of the GCC countries undertake successful efforts to diversify their economies away from dependence on hydrocarbon industries. These diversified growth sectors, such as finance, logistics, aviation, communications, healthcare and tourism provide abundant business opportunities. Liberal climates towards foreign cooperation, investment and modernization result in extensive diplomatic and commercial relations with other countries.
Arguably the most important article of the GCC charter is Article 4, which states that the alliance was formed to strengthen relations among its member countries and to promote cooperation among the countries’ citizens. The GCC also has a defense planning council that coordinates military cooperation between member countries. The highest decision-making entity of the GCC is the Supreme Council, which meets on an annual basis and consists of GCC heads of state. Decisions of the Supreme Council are adopted by unanimous approval. The Ministerial Council, made up of foreign ministers or other government officials, meets every three months to implement the decisions of the Supreme Council and to propose new policy. The administrative arm of the alliance is the office of the Secretariat-General, which monitors policy implementation and arranges meetings.
GCC agreements typically focus on either security or economic coordination. In terms of security coordination, policies have included the creation of the Peninsula Shield Force in 1984, a joint military venture based in Saudi Arabia, and the signing of an intelligence-sharing pact in 2004. The first significant deployment of the Peninsula Shield Force was in 2011 in Bahrain to guard government infrastructure against an uprising there during the Arab Spring protests. Economic coordination included attempts at economic union, though integrative agreements were often lackluster in comparison with policy coordination. An agreement to launch a single regional currency similar to the euro by 2010 saw little movement apart from the establishment of a monetary council in 2009. Coordination in tax policy proved fruitful, however: a customs union was implemented in 2015, and the member states began rolling out a value-added tax of 5 percent in 2018. Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates have tended to lead policy coordination. They were the first countries to send troops to Bahrain in 2011 and the first countries to levy the value-added tax.
The Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf (Arabic: ) , originally (and still colloquially) known as the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC, ), is a regional intergovernmental political and economic union consisting of all Arab states of the Persian Gulf – Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates – except Iraq.[2][3] The Charter of the GCC was signed on 25 May 1981, formally establishing the institution.[4]
All current member states are monarchies, including three constitutional monarchies (Qatar, Kuwait, and Bahrain),[5][6] two absolute monarchies (Saudi Arabia and Oman), and one federal monarchy (the United Arab Emirates, which is composed of seven member states, each of which is an absolute monarchy with its own emir). There have been discussions regarding the future membership of Jordan, Morocco, and Yemen.[7][8]
A proposal in 2011 to transform the GCC into a “Gulf Union” with tighter economic, political and military coordination was advanced by Saudi Arabia, a move meant to counterbalance the Iranian influence in the region.[9][10] Objections were raised against the proposal by other countries.[11][12] In 2014, Bahrain prime minister Khalifa bin Salman Al Khalifa said that current events in the region highlighted the importance of the proposal.[13] The Peninsula Shield Force is the military arm of the GCC, formed in 1984.
In order to reduce their future dependence on oil, the GCC states are pursuing unprecedented economic structural reform.
List Of Six Arab GCC (Or AGCC) Countries (Gulf Countries), Citizen Nationalities, Nations, Or Member States Is Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, UAE. Yemen And Iran Are Muslim Countries But Not GCC Members. Population Statistics, Foreign Expat Resident Percentages, Currency, Land Area, Other Figures And Data.
- Bahrain – or Kingdom of Bahrain
- Kuwait
- Oman – or Sultanate of Oman
- Qatar
- Saudi Arabia – or Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA)
- UAE – United Arab Emirates
Countries Not Part Of The GCC
Egypt – is not a GCC country. Is an Arab Muslim country (mostly, also a significant Christian population).
Iran (Islamic Republic of Iran) – is a Muslim country. Is not an Arab country (is Persian, only about 2% of the population is Arab). Has a coast on the Persian Gulf (Arabian Gulf).
Iraq – is an Arab Muslim country. Has an Arabian Gulf coast (just barely, between Kuwait and Iran).
Jordan – is an Arab Muslim country but not part of the GCC.
Palestine – is not a GCC country.
Yemen – is an Arab Muslim country but does not have a coast on the Arabian Gulf (Persian Gulf).
Total and average figures for GCC countries
Total GCC Population Is About 42-45 Million As Of July 2014 (Using An Estimate Of About 7-8m For The UAE). About 60% Of The Total Is For Saudi Arabia.
| Bahrain | Kuwait | Oman | Qatar | Saudi Arabi (KSA) | UAE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capital | Manama | Kuwait City | Muscat | Doha | Riyadh | Abu Dhabi |
| Ruler | Hamad Bin Isa Al Khalifa | Sheikh Sabah Al Ahmad Al Jaber Al Sabah | Sultan Qaboos Bin Said Al Said | Sheikh Tamim Bin Hamad Al Thani | King Salman bin Abdulaziz Al Saud | Shaikh Khalifa bin Zayed Al Nahyan |
| Title, date | King, since Mar 1999 | Emir from Jun 2013 | King from 23 Jan 2015 | President, since Nov 2004 | ||
| Population2,3 | 1,314,089 (2014, CIA) | 2,742,711 (2014, CIA) | 3,219,775 (2014, CIA) | 2,123,160 (2014, CIA) | 27,345,986 (2014, CIA) | 9.2m (2013, World Bank)4 |
| Population2 | 1,106,509 (July 2008, CIO) | 3,996,899 (2014, PACI) | 2,224,583 (2015, QSA) | 8,264,070 (2010, NBS)4 | ||
| Land Area | 741 sq km | 2.15m sq km | 83,600 sq km | |||
| Currency | Bahraini Riyal | Kuwaiti Dinar | Omani Riyal | Qatari Riyal | Saudi Riyal | Dirham AED |
| Citizens | Bahrainis | Kuwaitis | Omanis | Qataris | Saudis or Saudi Arabians | Emiratis |
| Citizenship | Father, not birthplace | Father, not birthplace | Father, not birthplace | Father, not birthplace | Father, not birthplace | Father, not birthplace1 |
| Percentage expats5 | 55% (UN, 2013) | 70% (PACI, 2014) | 30% (UN, 2013) | 85% (2014, estimate) | 30% (UN, 2013) | 80-90%5 |
| Flag | ||||||
| Airlines | Gulf Air6 | Kuwait Airways6 | Oman Air | Qatar Airways | Saudia6 | Etihad Airways6 |
- See country notes and updates section (sections) below.
- Population figures are often unreliable, a second source might be given for comparison.
- https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2119rank.html – CIA World Factbook population figures reference.
- UAE population estimate of 5,628,805 given by the CIA for Jul 2014 is misleading as it is based on a UAE NBS figure from the 2005 census, which was probably too low at the time anyway (a number of residents did not participate in the census). The World Bank 2013 estimate is possibly too high but there is no question the population has increased substantially since 2005. The UAE NBS figure for 2010 might be a reasonable estimate for 2014-2015. As of Jan 2015, the most recent population figures released by the NBS (the official government statistics department) were 8.2m as a 2010 estimate, and 5.6m for the 2005 census.
- Variation of up to 5% higher or lower is common depending on which source, also varies over time but not as much. For the UAE, UN 2013 estimate is 80%, UAE NBS 2010 estimate is 89%. But trend is decreasing proportion of citizens, increasing proportion of expat foreigners, so UN estimate is likely to be too low.
- Airline notes (commercial operators with scheduled flights only):
- Etihad Airways is based in Abu Dhabi, and is (or claims to be) the national carrier of the UAE. Other UAE airlines include Air Arabia (Sharjah), Emirates Airline (Dubai), FlyDubai (Dubai), RAK Airways (Ras Al Khaimah, services suspended 31 Dec 2013), Rotana Jet (Abu Dhabi).
- Gulf Air was originally the national or flag carrier for Bahrain, Oman, Qatar, and Abu Dhabi emirate, which jointly owned the airline. From 2002-2007 Oman, Qatar, and Abu Dhabi withdrew from the partnership leaving Gulf Air the national carrier solely for Bahrain, and owned by Bahrain.
- Kuwait Airways is the national carrier of Kuwait. Other operators include Jazeera Airways.
- Saudia (Saudi Arabian Airlines) is the flag carrier of Saudi Arabia. Other operators include FlyNas (previously Nas Air).
List Of GCC Countries The GCC has Six Members.
The Kingdom of Bahrain – Its 1.4 million people enjoy a GDP per capita of $51,800. Its economy grew by 2.5% in 2017. It has 124.5 million barrels of proven oil reserves.
Kuwait – Its 2.9 million residents enjoy the 11th highest standard of living in the world. Its GDP per capita is $69,700. The country holds 6% of the world’s oil reserves. That’s 101.5 million barrels.
The Sultanate of Oman – Its oil reserves are only 5.4 million barrels. It is shifting to tourism to improve the lifestyle of its 3.4 million residents. Its GDP per capita is $45,500.
Qatar – The second richest country in the world, with a GDP per capita of $124,900 for each of its 2.3 million residents. It has 25.2 billion barrels of proven oil reserves and 13% of the world’s natural gas reserves.
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia – The largest of the GCC countries with 28.5 million people. It has 16% of the world’s proven oil reserves. That’s 266.5 million barrels. Its GDP per capita is $55,300.
The United Arab Emirates – Its 6 million people enjoy a per capita GDP of $68,00. That’s thanks to a diversifying economy that includes Dubai and the world’s tallest building, the Burj Dubai Khalifa. Dubai is the second-largest of the seven city-states in the UAE. Abu Dhabi is the largest. The UAE has 97.8 million barrels of proven oil reserves.
Which Countries Are Part of the GCC?
The GCC comprises six member states, each contributing uniquely to the region’s development:
1. The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia is the largest GCC country by land area and economy. It is a dominant player in the global oil market, producing approximately 10% of the world’s crude oil. Saudi Arabia also serves as the spiritual hub of the Islamic world, being home to Mecca and Medina.
- Capital: Riyadh
- Key Contributions: Oil production, renewable energy initiatives, and Vision 2030 reforms.
- Population: Over 35 million (2023 estimate).
2. The United Arab Emirates (UAE)
The UAE is a global hub for trade, tourism, and finance. It comprises seven emirates, including Dubai and Abu Dhabi, both of which are internationally recognized for their innovation and infrastructure.
- Capital: Abu Dhabi
- Key Contributions: Diversified economy, aviation, and real estate.
- Population: Over 9 million (2023 estimate).
3. The State of Kuwait
Kuwait is renowned for its wealth derived from substantial oil reserves. The country’s sovereign wealth fund, one of the oldest and largest in the world, highlights its economic stability.
- Capital: Kuwait City
- Key Contributions: Oil exports and strategic investments.
- Population: Approximately 4.5 million.
4. The State of Qatar
Qatar boasts one of the highest GDP per capita figures globally, largely due to its natural gas reserves. It is also known for hosting major international events, including the FIFA World Cup 2022.
- Capital: Doha
- Key Contributions: LNG exports, sports diplomacy, and education.
- Population: Around 2.9 million.
5. The Sultanate of Oman
Oman’s economy is heavily influenced by oil and natural gas exports, but it has been diversifying its economic base in recent years. Its rich cultural heritage and tourism industry are also noteworthy.
- Capital: Muscat
- Key Contributions: Logistics, tourism, and renewable energy projects.
- Population: Approximately 4.5 million.
6. The Kingdom of Bahrain
Bahrain is the smallest GCC member but holds significant importance as a financial center. It is well-regarded for its open economy and vibrant banking sector.
- Capital: Manama
- Key Contributions: Banking, financial services, and aluminum production.
- Population: Over 1.7 million.
Economic Significance of GCC Countries
The GCC countries collectively contribute to approximately 25% of the world’s proven oil reserves. Additionally, they are major exporters of natural gas. The region’s strategic location, connecting Asia, Europe, and Africa, further enhances its economic significance.
- Trade Agreements: GCC countries benefit from free trade agreements and economic pacts that boost regional and global trade.
- Infrastructure Projects: Large-scale investments in transportation, healthcare, and energy infrastructure strengthen economic integration.
Key Industries
- Energy: Oil and gas dominate exports.
- Finance: Dubai, Bahrain, and Doha are major financial hubs.
- Tourism: The UAE, Oman, and Qatar attract millions of visitors annually.
- Technology: Investments in AI, blockchain, and renewable energy are on the rise.
Cultural and Historical Importance of GCC Nations
The GCC countries share deep cultural and historical ties rooted in Arab traditions, Islamic values, and a common language. These shared elements foster strong diplomatic and social bonds.
- Islamic Heritage: Mecca and Medina are pivotal to the Islamic faith.
- Festivals and Traditions: GCC nations celebrate traditional festivals like Eid and Ramadan with cultural fervor.
- Architecture: The blend of modern skyscrapers and traditional designs reflects the region’s unique identity.
Future Goals of the GCC
1. Economic Diversification
Reducing reliance on oil is a priority. Member states are investing in renewable energy, technology, and tourism.
2. Sustainable Development
GCC countries aim to implement environmentally friendly practices, including solar energy projects and waste management systems.
3. Strengthening Regional Security
Collaboration on defense strategies ensures the stability and safety of the Gulf region.
4. Enhancing Global Influence
By hosting international events and fostering global partnerships, GCC nations aim to boost their diplomatic and economic influence.